Photoshop Masks
Masking is the process of only showing part of an image on top of another. I'm here to show you all a tutorial about how to do this, and some of its practical uses.
How to make a Layer Mask
So, open up your first image and second image in Photoshop Elements. Select all of the second image, go to Edit > Copy. Return to the first image, and go to Edit > Paste. Now, the second image should appear as a new layer above the original image.
In order for the mask to work, both images have to be "layers" and not "backgrounds". If you see that the original image is labeled as a background in the layers palette, select it and go to Layer > New > Layer from Background.
For the next step, things will be different depending on what program you use.
For Photoshop Elements:
If you use the full version of Photoshop, you can skip to the next section. As opposed to other programs, Photoshop Elements does not come with the natural ability to add a layer mask. However, it is still possible to recreate the same effect, and it is actually incredibly easy to do so.
Select the bottom layer in the layers palette. Press the "adjustment layer" button, and select anything (it doesn't really matter. In this example, I used "solid color.") Press "OK" when the dialogue window pops up.
This time, select the top layer. Go to Layer > Group with previous.
You see the white thumbnail next to the adjustment layer? This is the layer mask canvas. Now you can skip the instructions for other versions and go right to the next step.
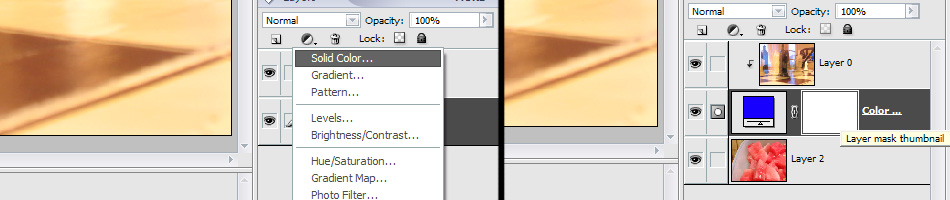
Notice the picture of the layer mask on the right.
For Photoshop (full version):
Click on the top layer. Now, press the layer mask button. It's that simple. Now, the white thumbnail next to the top layer is your layer mask canvas.
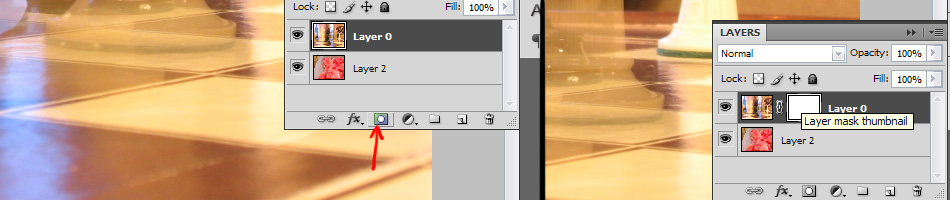
See, wasn't that simple?
Drawing in the Mask
There are a few things you should know about how layer masks work. Firstly, to edit one, you first have to click on the layer mask thumbnail. Then, you can draw as you normally would, add gradients, etc. But make sure you draw black-and-white pictures on the layer mask canvas. White means that the layer the mask is applied to will be visible in that area. Black means the layer the mask is applied to will be invisible in that area. Various shades of grey fall in between.
Some examples:

A gradient mask will look like this.

The blurred circular mask will result as shown.
Some practical uses
Soft Focus or Tilt Shift
One of the uses that I take advantage of the most often is the soft focus effect. Basically, you have the same image on both two layers, except that on the one you're masking, you have applied filter > blur > Gaussian blur. From there, you apply the layer mask, making it so that there is a blurred hole where your subject is, allowing for the focused image to show through. An example or two:

A tilt-shift effect.

A tilt-shift effect when applied to a photo.
Greenscreening
Do you ever wonder how you put a photo of you on top of another picture? Well, here's how. Basically, you just have the photo of you as the top layer, and make the layer mask just a white silhouette of you on top of a black background. An example:

Notice how the mask in the corner is a white silhouette with a black background.
Conclusion
Try experimenting with layer masks and you'll find that there's an awful lot you can do with them. If you make things fade into nothingness with a mask, you can create the illusion of a reflection on a shiny surface. With practice, you can make some really awesome effects.
</david>